Automated SPAM Detection: Filter and Block Conversations at Scale
botBrains introduces automated SPAM detection to help teams block unwanted conversations and protect insight quality. Define rules that automatically filter, label, and block.
Liam van der Viven
Co-Founder & CTO at botBrains
Today we're excited to announce automated SPAM detection and blocking. This feature enables teams to define rules that automatically filter unwanted conversations and protect the quality of their insights. The result: support teams focus on genuine customer inquiries while SPAM messages from marketplace notifications, known problem domains, and suspicious user patterns are automatically blocked.
Why Automated SPAM Detection?
Imagine an e-commerce shop receiving order confirmations through major marketplaces like Amazon, eBay, or PayPal. Each order generates notifications forwarded to the support channel. The support team spends valuable time daily reviewing and closing these automatic notifications - time better spent on real customer inquiries.
Automation isn't control, but protection of team resources from predictable, repetitive tasks. It's about focus and efficiency.
Three reasons why automated SPAM detection is fundamentally important:
Protecting Team Productivity: Support agents shouldn't spend time on obvious SPAM. Automatic filtering means qualified staff can focus on complex customer inquiries that require real expertise.
Consistent Quality Assurance: Manual SPAM moderation is error-prone and inconsistent. Automatic rules apply the same criteria to every conversation, ensuring no SPAM message slips through and genuine customer inquiries aren't accidentally blocked.
Scalability: As your business grows, so does SPAM volume. Automation scales with you without requiring additional moderation resources.
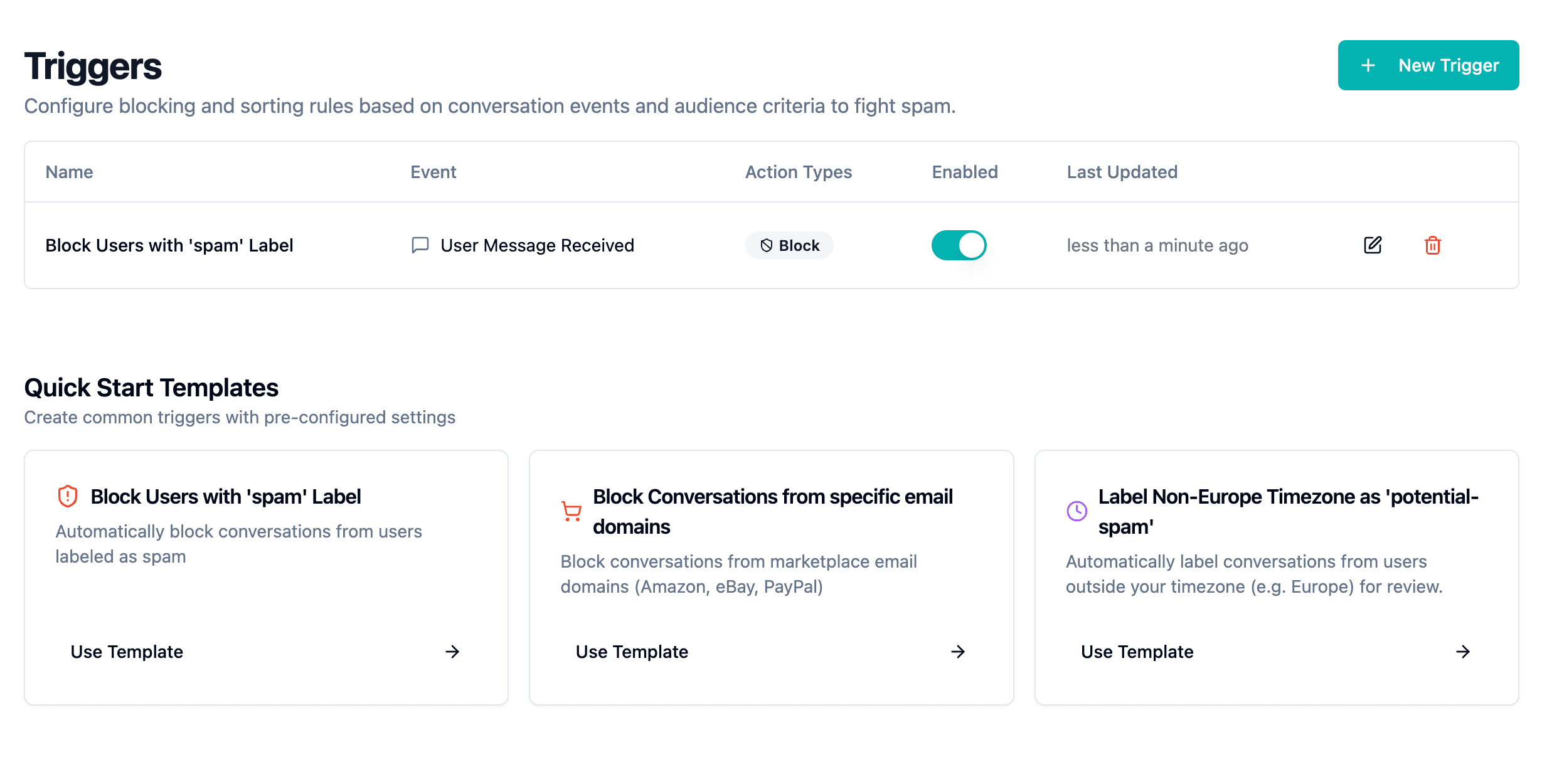
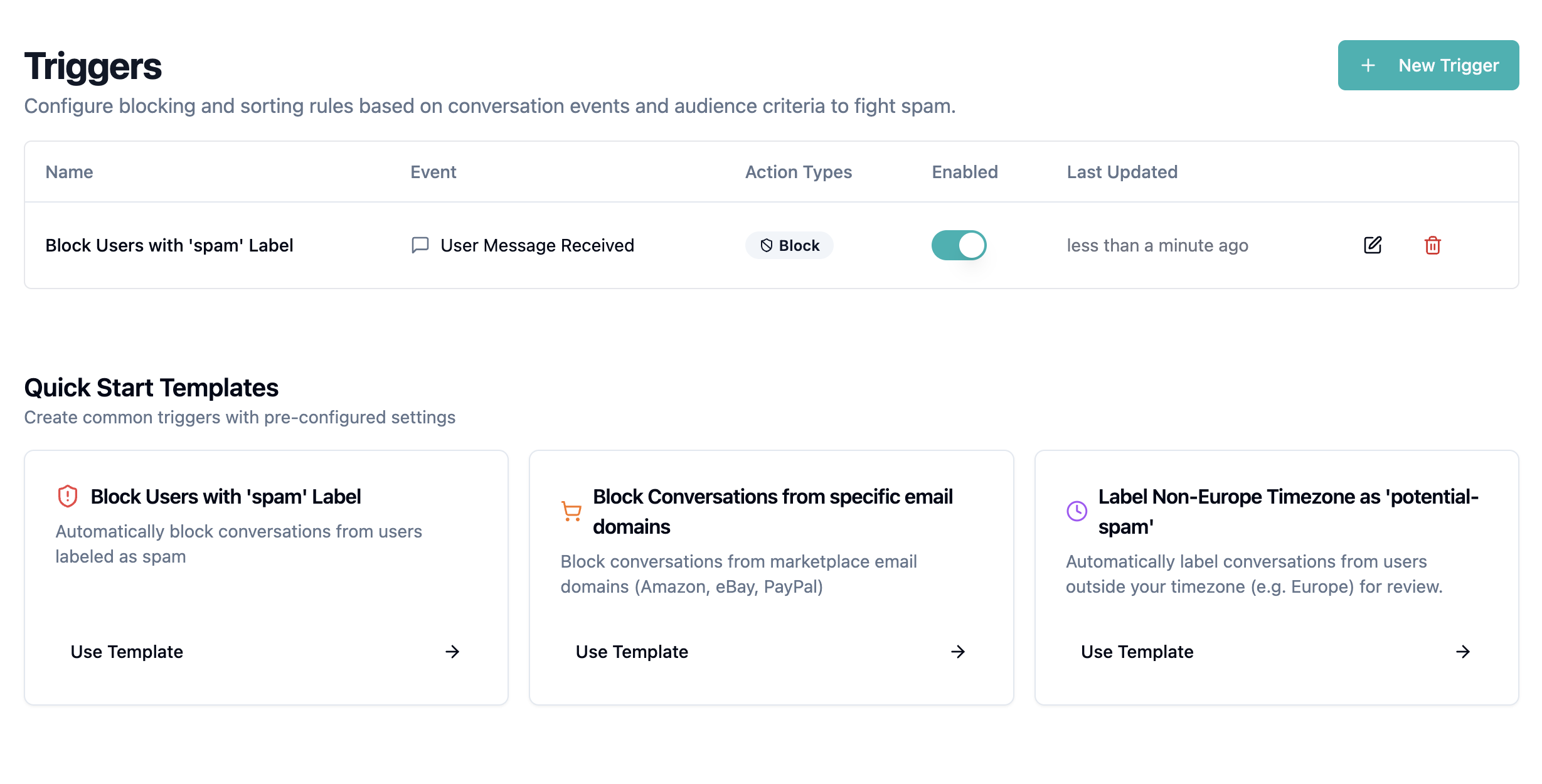
Trigger System
The trigger system consists of two parts: "When" defines which events and audience criteria trigger a rule. "Then" defines which actions are automatically executed. Events like "User Message Received" combined with audience filters like email domains or labels create precise automation rules.
You define rules with a visual builder:
"When" - Event & Audience:
- Events: Currently "User Message Received" (more coming)
- Audience Builder: The same powerful query builder as audience pages
- Nested rule groups with AND/OR/NOT combinations
- Fields: user.labels, user.email, user.timezone, and more
- Operators: in, ends_with, begins_with, and others
"Then" - Actions:
- Block conversation: Stops the conversation before it reaches your insights
- Assign label: Automatically marks conversations, messages, or users
- Unassign label: Removes labels based on conditions
- Multi-actions: Combine multiple actions per trigger
Use Cases
Block Marketplace Notifications
E-commerce teams receive hundreds of automatic notifications daily from platforms like Amazon, eBay, or PayPal. These messages contain no genuine customer inquiries and degrade the quality of your insights.
Example: An online retailer with 200 daily orders creates a trigger: If the email address ends with @amazon.com, @ebay.com, or @paypal.com, block the conversation automatically. The team saves up to 1 hour daily previously spent manually removing these conversations. Metrics show over 150 conversations per day are automatically filtered.
Block Known SPAM Users
Teams discover SPAM patterns and manually label problem accounts. A trigger automates the follow-up action: If a user has the label "spam", block all future messages from that user. This creates a growing blocklist without repeated manual interventions.

Scenario: A SaaS company regularly receives SPAM from known problem accounts. A support agent reviews a suspicious conversation, confirms SPAM, and assigns the "spam" label to the user. From that moment on, a trigger automatically blocks all future messages from that user. The team builds an organic blocklist that grows stronger with each SPAM identification.
Geographic Filters for Fraud Prevention
Companies primarily operating in certain regions often see SPAM from unexpected timezones. Geographic filters help identify suspicious patterns.
Example: A German company serves mainly European customers. A trigger automatically labels all conversations from users outside European timezones as "potential-spam" for manual review. This doesn't immediately block all messages but flags suspicious patterns for team review - a cautious approach that avoids false positives.
Multi-Action Workflows
Triggers support multiple actions to automate complex workflows.
Scenario: A financial services company wants to block conversations from certain competitor domains while tracking them for later analysis. A trigger detects email addresses from known competitors, assigns the "competitor-inquiry" label, assigns a second "blocked-automatically" label, then blocks the conversation. The marketing team exports all "competitor-inquiry" conversations monthly to understand market positioning, while these messages never reach the support insights.
Quick-Start Templates
We provide three pre-configured templates for the most common scenarios:
SPAM Blocker: Automatically blocks conversations from users with the "spam" label. Clicking the template loads the configuration directly into the editor.
Marketplace Filter: Blocks notifications from Amazon, eBay, and PayPal. Ready to use immediately for e-commerce teams.
Geographic Filter: Labels conversations from users outside European timezones as "potential-spam" for review.
Each template can be customized as a starting point. Add additional domains, change timezone filters, or combine multiple templates into a comprehensive SPAM strategy.
Conversation Filter Health Metrics
Automation without visibility is risky. Our metrics dashboard shows how many conversations are being filtered, SPAM trends over time, and trigger effectiveness. Teams immediately see if their rules are working or need adjustments.
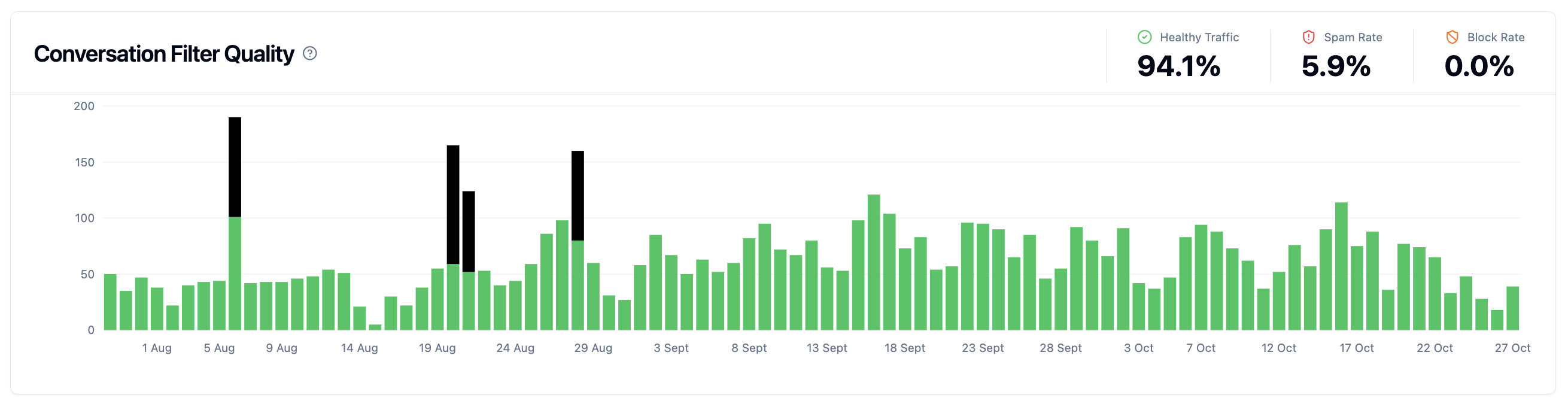
The new dashboard offers:
ConversationHiddenChart: Visualizes blocked and hidden conversations over time. Shows SPAM volume trends and helps detect sudden changes.
Metric Cards: Summary KPIs about filter effectiveness. See at a glance how many conversations were automatically blocked and how much time your team saved.
Automation Validation: When you create a trigger to block marketplace emails, the dashboard shows that 50 conversations were automatically filtered this week. You see the ROI of your automation in real-time. If the dashboard suddenly shows zero blocks, you know something might be misconfigured.
Batch SPAM Management
Besides automatic triggers, teams can mark multiple conversations as SPAM in one action:
The batch selection toolbar in the conversation list offers a "Mark as SPAM" action. Select upto 120 conversations, confirm the action in the confirmation dialog, and all are marked as hidden with a single API call. This is especially useful when you discover a new SPAM vector and need to quickly clean up historical conversations.
Why SPAM Detection Is So Difficult
The biggest risk in automated SPAM detection isn't letting SPAM through - it's blocking a real customer.
Imagine: A potential customer from an unusual timezone, with an unfamiliar email domain, writes their first message. Perhaps their language pattern is unusual or their inquiry doesn't fit typical patterns. If your SPAM filter is too aggressive, you block exactly this person - and the first touchpoint with your company becomes a negative experience. This customer will never return.
The goal is a false positive rate of nearly 0%. A blocked SPAM costs you nothing. A blocked customer costs you everything.
That's why our trigger system is deliberately designed to be cautious:
Precise criteria over broad filters: Filters like "email ends with @amazon.com" are absolutely safe - no real customer uses that address. Geographic filters, however, should only be used for flagging, not automatic blocking.
Label-first, block-later: The "potential-spam" strategy allows manual review before final blocking. Teams learn patterns without taking risks.
Combined signals: Multiple weak signals (unusual timezone + new domain + short message) can be stronger together than a single signal. Multi-condition triggers create safety.
Metrics for validation: The dashboard shows not only blocked conversations but also helps discover false positives. When suddenly many conversations are being blocked, that's a warning signal.
Data-Driven Automation
Teams lose valuable time daily to predictable SPAM, said Liam van der Viven, Co-Founder & CTO of botBrains. A support agent reviews 20 Amazon notifications, clicks Close 20 times - that's 10 minutes of wasted time better spent on complex customer inquiries. Automated SPAM detection gives teams that time back.
But automation without visibility is dangerous. That's why we built the metrics dashboard. Teams see exactly how many conversations are being filtered, can identify trends, and adjust their rules based on actual data. If suddenly 200 conversations per day are blocked instead of the usual 50, you immediately know that either a new SPAM vector has appeared or your rule has become too aggressive. This feedback loop transforms automation from a set and forget tool into a continuous improvement process.
Getting Started
The trigger system is now available for all customers. Go to Settings → Triggers to create your first automation rule. Quick-start templates help you get started within minutes.
Metrics are automatically integrated into your project metrics page. No configuration required - simply open metrics and see your conversation filter health.
Conclusion
Automated SPAM detection protects team productivity and insight quality. Through precise trigger rules, you automatically filter unwanted conversations while metrics provide transparency about filter effectiveness. Teams reclaim time, focus on genuine customer inquiries, and scale their support operations more efficiently.